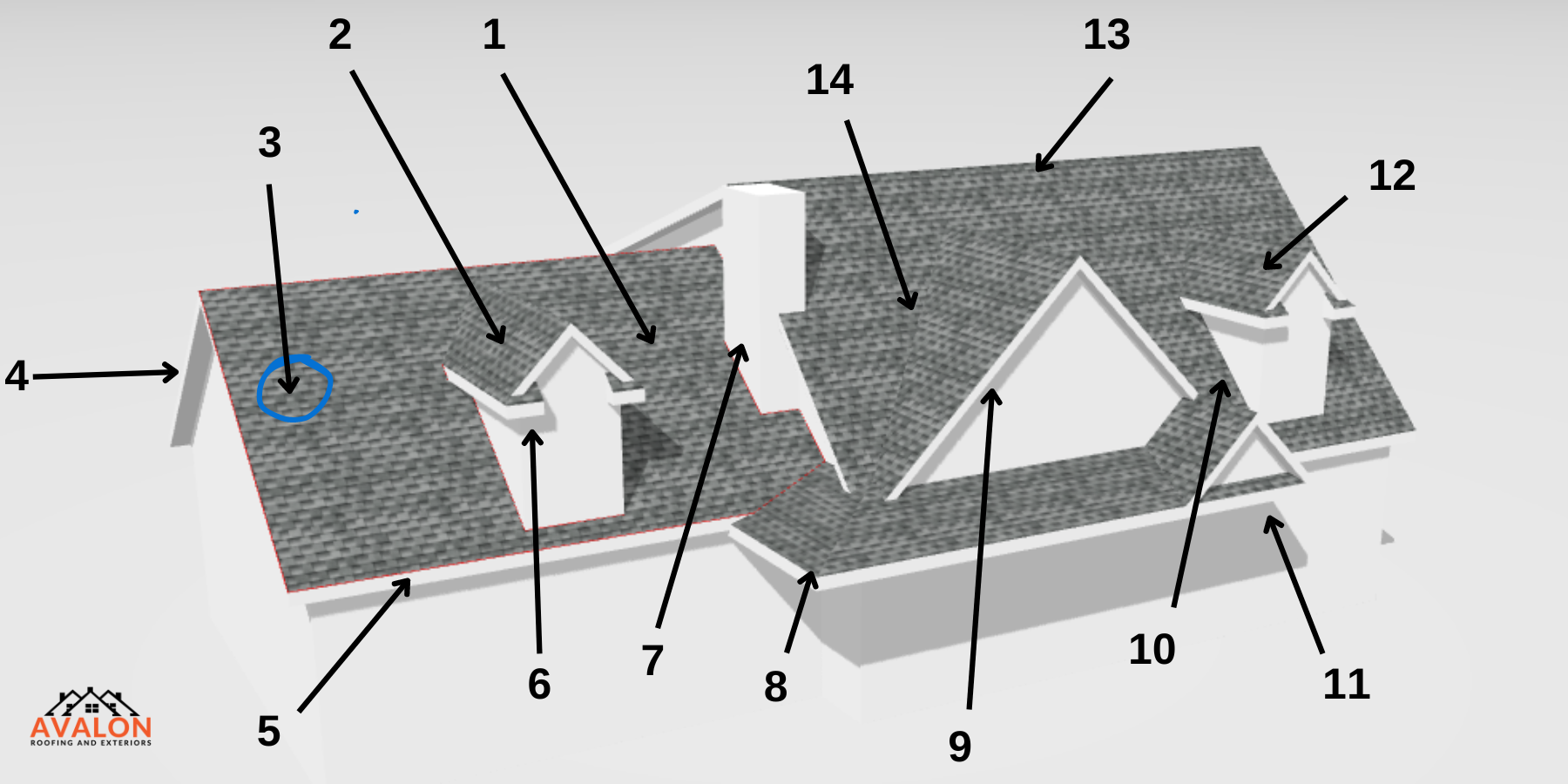
The above diagram is labeled with some of the architectual elements of a sloped roof as described in the chart below.
| ROOF COMPONENT | DESCRIPTION: | |
| 1 | Plane | This is the surface of the roof. It may be flat, pitched or on an angle. It is also called the field of the roof. |
| 2 | Facet | A facet is one section (plane or surface) of a multi-sectioned roof. |
| 3 | Roof Covering | The most visible part of the roofing system. Roof coverings tend to come in panels/tiles that come in many different materials. |
| 4 | Rake Edge | The Slanting edge of a roof. |
| 5 | Eave/Eave Edge | The lower edge of a roof (often overhanging beyond the edge of the house) |
| 6 | Cornice Return | An architectural detail that occurs where the horizontal cornice of a roof connects to the rake of a gable. |
| 7 | Chimney/Chimney Flashing | An architectural ventilation structure made of masonry, clay or metal. The chimney flashing is a crucial component of your roof system, consisting of a waterproof layer/metal flashing placed where the chimney and rooftop intersect. |
| 8 | Hip | The external angle formed where two adjacent sides of a roof meet and project outward |
| 9 | Gable | A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. |
| 10 | Sidewall | A junction between a wall and a sloped portion of a roof |
| 11 | Full Cornice return | An architectural detail that occurs where the horizontal cornice of a roof connects to the rake of a gable. |
| 12 | Dormer | A roofed structure, often containing a window, that projects vertically beyond the plane of a pitched roof. |
| 13 | Ridge/Peak | the horizontal line running the length of the roof where the two roof planes meet. This intersection creates the highest point on a roof, sometimes referred to as the peak. |
| 14 | Valley | Where two sloping roof sections meet at their base. Water collects in a valley to flow off the roof |

