| What is Pitch? | ||
| Roof pitch, also known as slope, is a roof’s steepness, or how many inches it rises vertically for every 12 inches it extends horizontally. It’s expressed as a ratio, with the higher the first number (rise) in the ratio, the steeper the roof. For example, a roof with a pitch of 4/12 rises four inches for every 12 inches horizontally. A flat roof has a pitch of zero | ||
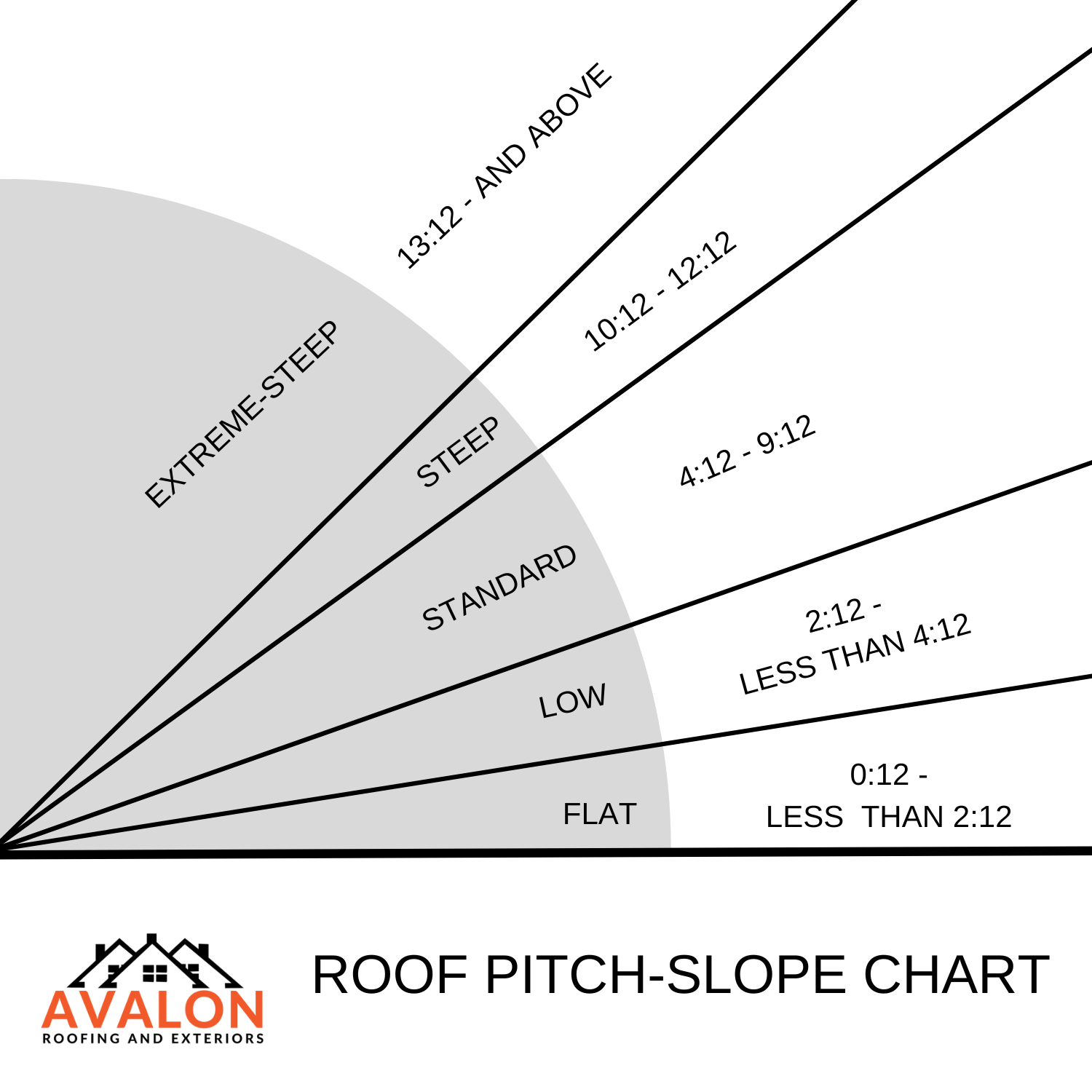
| TYPES OF PITCH: | ||
| Flat | From 0:12 to less than 2: 12 | |
| Low Slope | From 2:12 to less than 4:12 | |
| Steep Slope (Standard) | 4:12 TO 9:12 | |
| Steep Slope (Steep) | 10:12 TO 12:12 | |
| Steep Slope (Extreme) | 13:12 and Above | |
| ROOF PITCH | ANGLE OF THE SLOPE | PITCH TYPE |
| 0:12 Pitch | 0° | FLAT |
| 1:12 pitch | 4.76° | FLAT |
| 2:12 pitch | 9.46° | LOW |
| 3:12 pitch | 14.04° | LOW |
| 4:12 pitch | 18.43° | STEEP |
| 5:12 pitch | 22.62° | STEEP |
| 6:12 pitch | 26.57° | STEEP |
| 7:12 pitch | 30.26° | STEEP |
| 8:12 pitch | 33.69° | STEEP |
| 9:12 pitch | 36.87° | STEEP |
| 10:12 pitch | 39.81° | STEEP |
| 11:12 pitch | 42.51° | STEEP |
| 12:12 pitch | 45° | STEEP |
| How does the pitch affect the roofs function? | ||
| Roof pitch is important for a number of reasons, including: | ||
| Shedding water | ||
| Steep roofs are better at shedding water and preventing moisture buildup, which can help prevent leaks, water damage, and mold or mildew growth. | ||
| Flat Roofs tend to hold water and can require drains. Also have a higher chance of debris accumulation. | ||
| Shedding debris: | ||
| Steep roofs make it harder for debris like leaves, branches, and snow to accumulate, which can reduce the risk of clogs and water damage. | ||
| Flat Roofs are more likkely to hold debris and require more regular maintenance | ||
| Temperature control: | ||
| Steep roofs are exposed to less direct sunlight, which can help keep a house cooler in warmer climates. In the winter, pitched roofs can also help reduce heating costs. | ||
| Roof replacement | ||
| Steeper roofs can take longer and cost more to replace because installers need to take more safety measures | ||
| For Steep Steep Roofs- the price of installation increases. | ||
| For Extreme Steep Roofs- extra precautions are taken during the installation process including additional nails and hand sealing shingles. | ||
| Roof coverings: | ||
| It’s the most visible part of the roofing system and the type of roof coverings are determined by the pitch of the roof. | ||
| Flat/Low Slope roofs require Membrane Roofing which is a roof system that creates a continuous watertight covering to protect the interior of a building | ||
| Sloped roof coverings: Slope roof coverings tend to be panels/tiles that come in many different materials. | ||
| How is roofing measured? | ||
| by the SQUARE | ||
| What is a SQUARE? | ||
| A unit of measurement that’s equal to 100 square feet of roof surface area. |
The remainder of this course will focus primarily on Sloped Roofs.

